Electrons in 1.58 dimensions? What the frac!
Utrecht physicists build fractal shape out of electrons
In physics, it is already well-known that electrons behave very differently in three dimensions (cube), two dimensions (sheet) or one dimension (wire). These behaviours give rise to different possibilities for technological applications and electronic systems. But what happens if electrons live in 1.58 dimensions – and what does it actually mean to live in 1.58 dimensions? Theoretical and experimental physicists at Utrecht University investigated that in a new study that will be published in Nature Physics on 12 November.
It may be difficult to imagine 1.58 dimensions, but the idea is more familiar to you than you think at first glance. Non-integer dimensions, such as 1.58, can be found in fractal structures, such as your lungs. A fractal is a self-similar structure that scales in a different way than normal objects: if you zoom in, you will see the same structure again. For example, a small piece of Romanesco broccoli typically looks similar to the whole head of broccoli. In electronics, fractals are used a lot in antennas for their properties of receiving and transmitting signals in a large frequency range.
Electronic nanoscale fractals
A relatively new topic in fractals is the quantum behaviour that emerges if you zoom in all the way to the scale of electrons. Using a quantum simulator, Utrecht physicists Sander Kempkes and Marlou Slot were able to build such a fractal out of electrons. The researchers made a ‘muffin tin’ in which the electrons would confine to a fractal shape, by placing carbon monoxide molecules in just the right shape on a copper background with a scanning tunneling microscope. The resulting triangular fractal shape in which the electrons were confined is called a Sierpiński triangle, which has a fractal dimension of 1.58. The researchers observed that the electrons in the triangle actually behave as if they live in 1.58 dimensions.
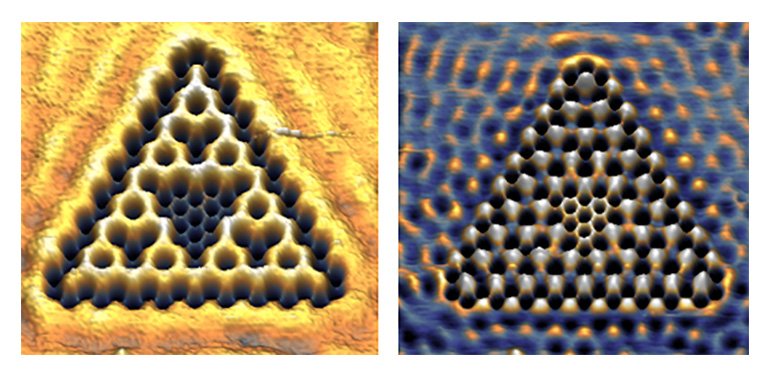
Electronic wavefunction
The results from the study show how bonding (left image) and non-bonding Sierpiński (right image) triangles are separated in energy, yielding nice opportunities for transmitting currents through these fractal structures. In the bonding case, the electrons are connected and can easily go from one place to another (high transmission), whereas in the non-bonding case they are not connected and need to “jump” to another place (low transmission). Also, by calculating the dimension of the electronic wavefunction, the researchers observed that the electrons themselves are confined to this dimension and the wavefunctions inherit this fractional dimension.
Interesting and groundbreaking
“From a theoretical point of view, this is a very interesting and groundbreaking result,” says theoretical physicist Cristiane de Morais Smith, who supervised the study together with experimental physicists Ingmar Swart and Daniel Vanmaekelbergh. “It opens a whole new line of research, raising questions such as: what does it actually mean for electrons to be confined in non-integer dimensions? Do they behave more like in one dimension or in two dimensions? And what happens if a magnetic field is turned on perpendicularly to the sample? Fractals already have a very large number of applications, so these results may have a big impact on research at the quantum scale. One thing is for sure: the future of electronics looks fractastic!”
Publication
Design and characterization of electrons in a fractal geometry
Sander N. Kempkes, Marlou R. Slot, Saoirsé E. Freeney, Stephan J.M. Zevenhuizen, Daniël Vanmaekelbergh, Ingmar Swart, Cristiane Morais Smith*
Nature Physics, 12 November 2018, DOI 10.1038/s41567-018-0328-0
* All authors are affiliated with Utrecht University
This research was funded in part by NWO Physics and the European Research Council.

